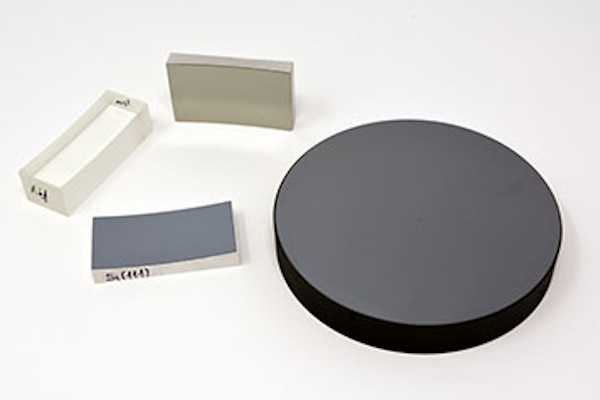

We supply X-ray monochromator crystals from Luxium Solutions (previously Saint Gobain Crystals). A monochromating crystal behaves in X-ray spectrometry as does a diffraction grating in optics therefore when rotated with respect to the incident beam it will diffract the spectral component in accordance with Bragg’s Law. The most important characteristic of a monochromating crystal is the double atomic spacing 2d, which defines the largest wavelength which can be diffracted. The St Gobain Crystals & Detector’s range of synthetic & naturally occurring monochromating crystals offers the widest possible variety of 2d spacing.
Our monochromating crystals are supplied as flat (unmounted or mounted on holders) for XRF spectrometers, or curved onto a holder to allow focusing for instruments such as microprobes, scanning electron microscopes, syncrotrons, XFEL, plasma physics.
Luxium Solutions (previously Saint Gobain Crystals) are the premier scintillation detection manufacture for ionizing radiation detection and provide high quality scintillation materials with superior resolution and advanced photo-sensor integration. Their core technology is the manufacturer of high performance engineering materials to solve their customers’ unique challenges. Luxium Solutions and Mi-Net have been working together in the UK and Ireland for over 30 years.

There are two main types of focusing configurations available:
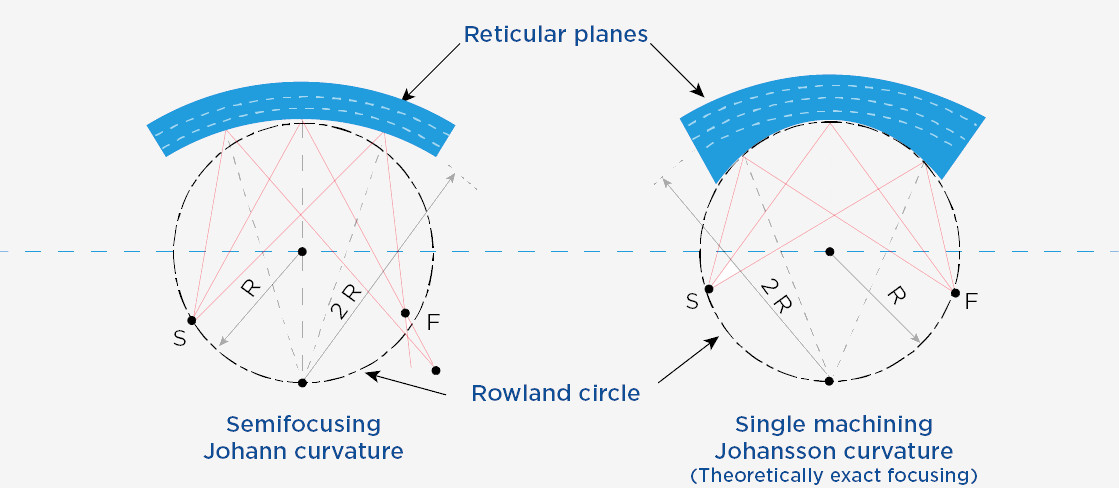
The Johann Geometry (semi-focusing)
A thin plate is produced by one of the two following methods:
The thin plate is then curved cylindrically and glued to a curved holder with approximate focusing.
The Johansson Geometry (exact focusing geometry)
Two different types of Johansson configurations, theoretically leading to perfect focusing, are considered:
The thin plate is either curved cylindrically, glued to a curved holder and one face is machined (single machining Johansson) or both faces are machined and then glued to a curved holder (double machining Johansson).
We will offer the best technique according to the type of crystal, its dimensions and the radius of Rowland circle to be achieved.
Other types of curvature may be investigated on request. Following designs can be made: Logarithmic spiral, Elliptical, Conical, Parabolic, Sphere, Toroidal
Manufacturing capabilities strongly depend upon the crystal nature, dimensions as well as the curvature radii.
| Crystal | Lithium fluoride | Quartz | Indium Antimonide | Silicon | Germanium | Pentaerythritol PET | Ammonium Dihydrogen Phosphate ADP | Beryl | Acid Phthalates | Crystal | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thallium TIAP | Rubidium RbAP | Potassium KAP | Cesium CsAP | |||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula | LiF | SiO2 | InSb | Si | Ge | C(CH2OH2) | NH4H2PO4 | 3BeO,Al2O36SiO2 | CO2HC6H4CO2TI | CO2HC6H4CO2Rb | CO2HC6H4CO2K | CO2HC6H4CO2Cs | Chemical formula | |||||
| Crystal system | Cubic | Hexagonal | Cubic | Cubic | Cubic | Quadratic | Quadratic | Hexagonal | Orthorhombic | Orthorhombic | Orthorhombic | Orthorhombic | Crystal System | |||||
| Parameters | Parameters | |||||||||||||||||
| a………………Å…. | 4.027 | 4.913 | 6.48 | 5.431 | 5.658 | 6.16 | 7.530 | 9.21 | 6.63 | 6.55 | 6.46 | 6.580 | a………………Å…. | |||||
| b………………Å…. | 4.913 | 6.16 | 7.530 | 9.21 | 10.54 | 10.02 | 9.61 | 10.752 | b………………Å…. | |||||||||
| c………………Å…. | 5.405 | 8.74 | 7.542 | 9.17 | 12.95 | 13.06 | 13.33 | 12.825 | c………………Å…. | |||||||||
| ß…………………… | ß…………………… | |||||||||||||||||
| Reflecting planes orientations | (200) | (220) | (420) | (1011) | (1010) | (111) | (111) | (220) | (111) | (220) | (002) | (101) | (1010) | (001) | (001) | (001) | (001) | Reflecting planes orientations |
| 2d in Å | 4.027 | 2.848 | 1.801 | 6.684 | 8.514 | 7.480 | 6.271 | 3.840 | 6.532 | 4.000 | 8.740 | 10.648 | 15.950 | 25.900 | 26.120 | 26.640 | 26.650 | 2d in Å |
| Usual surface finish | Cleaved or Treated | Treated | Treated | Polished | Polished | Polished | Polished | Polished | Polished | Polished | Cleaved or Treated | Polished or Treated | Polished | Cleaved | Cleaved | Cleaved | Cleaved | Usual surface finish |
| Reflectivity | Intense | Intense | Average | Good | Good | Intense | Intense | Average | Intense | Intense | Intense | Average | Average | Intense | Intense | Good | Good | Reflectivity |
| Calibration elements | Mo, Fe, Ti | Mo, Fe | Mo | Cu | Cu | Si | Cu | Cu | Cu | Cu | Al, Si | Mg | Mg | Na, Mg | Na | Na | Na | Calibration elements |
| Common Applications | From K to heavy elements | Heavy elements Lines splitting |
Heavy elements Lines splitting |
As Ge (111) |
As PET | Quantitative analysis of silicon | Extinction of even order spectral lines | Mg | Na and following elements | F to Al | Na to Al, up to F in emission probes | Na to Al, up to F in emission probes | Na to Al, up to F in emission probes | Common applications | ||||
We’re here and ready to provide information and answers to your questions
©Mi-Net 2023. All Rights Reserved.
Website by Fifteen.co.uk