Carbon fiber composite is composed of extremely strong carbon fibers bound by polymers, such as resin, epoxy or others. Its high strength-to-weight ratio and rigidity make carbon fiber composite an ideal material to be applied in a variety of industries, such as aerospace, automotive and civil engineering, sports goods and other consumer and technical applications. For example, its usage has been substantial increased in the most advanced aircrafts – The Airbus A350 XWB is built of 53% carbon fiber composite including wing and fuselage components, the Boeing 787 Dreamliner, 50%. It is also used extensively in high-end automobile racing and supercars.
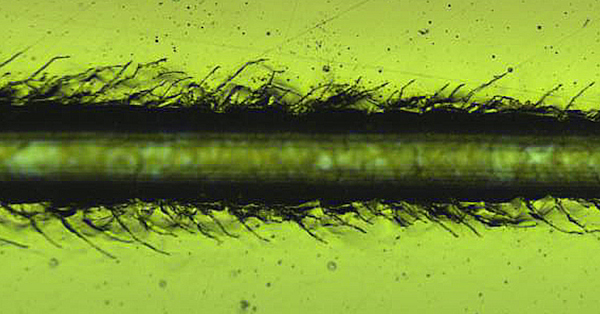
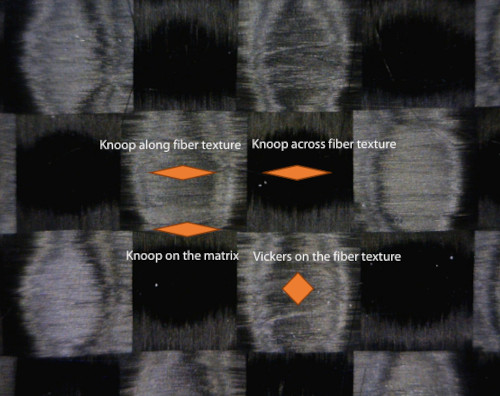
Unlike isotropic materials such as steel and aluminum, carbon fiber composite often has directional strength properties due to the texture layouts of the carbon fibers. Therefore, the local mechanical and tribological properties of the carbon fiber composite vary depending on the direction of the carbon fibers and the proportion of the carbon fibers relative to the polymer matrix at the test location.
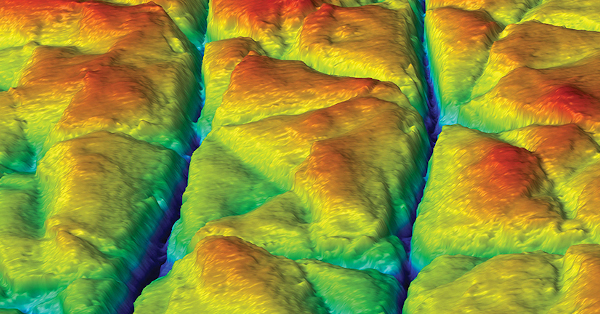
A reliable and accurate evaluation protocol of the local mechanical and tribological properties becomes vital for developing and comparing the carbon fiber composite in Quality
Control and Research and Development.
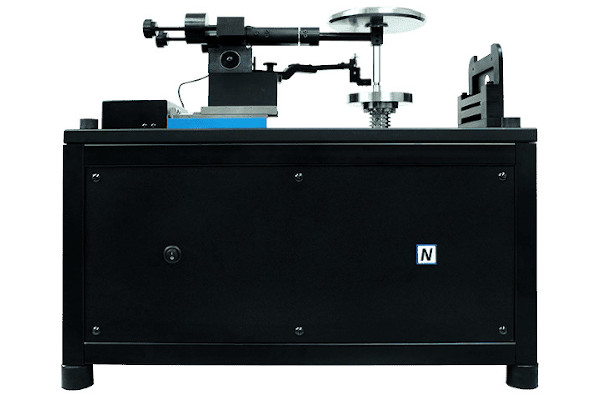
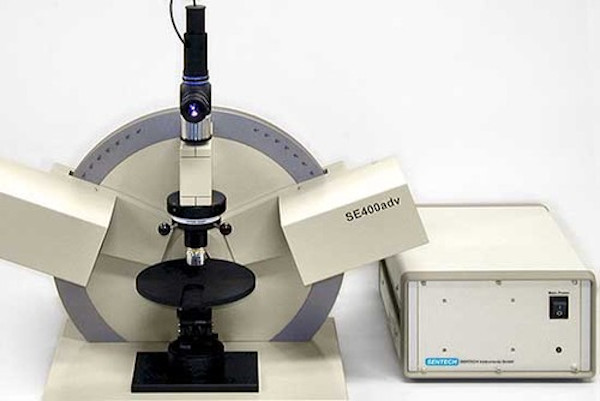
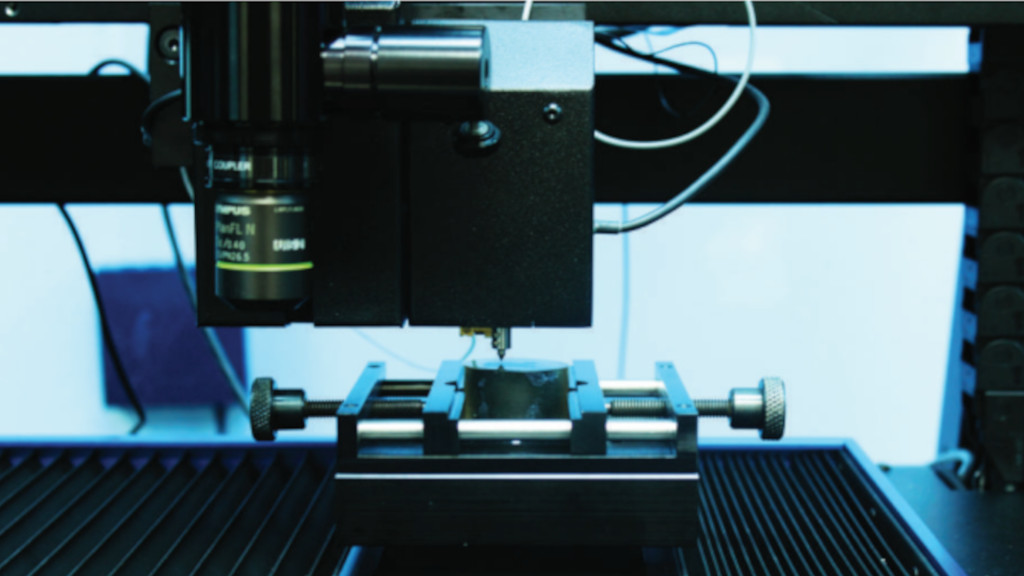
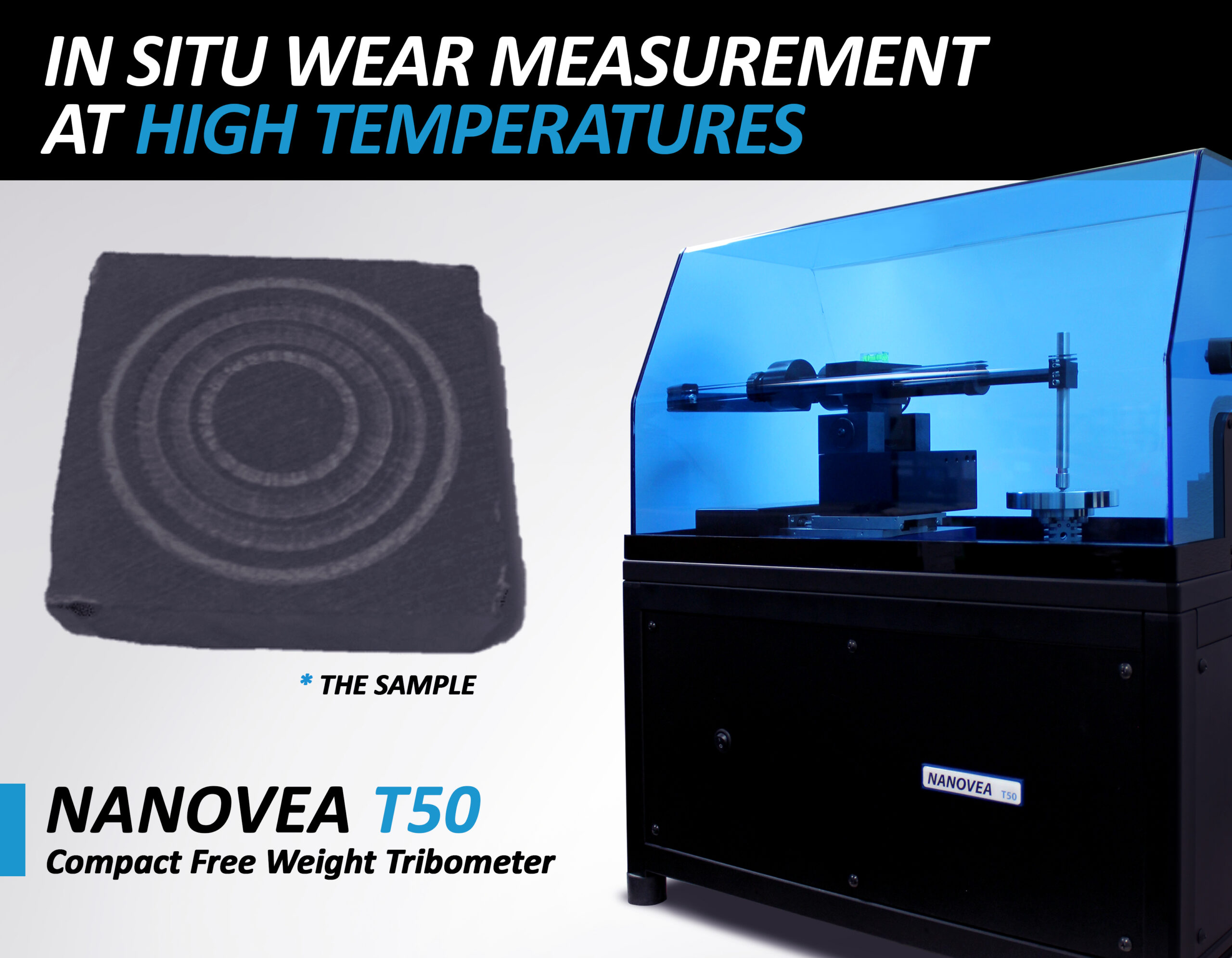
In this application note Nanovea use their Tribometer combined with their Optical 3D Profilometer and Mechanical Tester (set-up for indentation) to showcase the versatility and accuracy of the Nanovea instruments in testing composite materials with directional mechanical properties.
You can view the full application note here or you can request a pdf copy of this application note by clicking the Request Application Notes link below.